
updated 2000.11.30
Author Janez Puhan
Synchronous Demodulator
The circuit
To decode a message in amplitude modulated carriers, a waveform has to be multiplied with itself using a product demodulator. In many ways, a simple nonlinear device like a semiconductor diode can be used for this purpose. Its exponential characteristic can be mathematically expressed by a Taylor series. The message then is decoded by filtering out the quadratic term.
In applications like spectrum analysers and lock-in amplifiers, problems with higher order Taylor terms may occur. In this case, the diode should be replaced with a device having a parabolic characteristic, a junction field effect transistor for example. However, in zero-IF systems, dc terms have to be eliminated too. This is the area of synchronous demodulators.
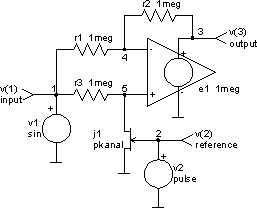
The input file
synchronous demodulator
.control
tran 50ns 10us
plot v(1)+3 v(2)/5-1 v(3)-3 xlabel t[s] ylabel 'input reference output[V]'
+ title 'TRAN analysis'
.endc
v1 1 0 dc 0 sin 0 1 550kHz
v2 2 0 dc 0 pulse 0 10V 0 0 0 1uS 2uS
r1 1 4 1meg
r2 4 3 1meg
r3 1 5 1meg
e1 3 0 5 4 1meg
j1 5 2 0 pkanal
.model pkanal pjf
.end
The results
